The Fluid Dynamic Strategy Required To Master 3/8 Vs 3/4 Sizing Computational Download Table
This document provides guidelines for piping hydraulics, fluid flow, line sizing, and material selection The two are often confused because they can use the same equations and design tools. It covers topics such as general fluid flow theory, flow characteristics in pipes, line sizing methods for both incompressible and compressible fluids, pump suction piping design, and material selection for piping
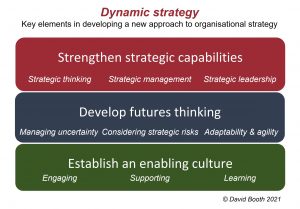
Dynamic strategy - Strategy Journeys
The document includes case studies and examples to demonstrate how to apply. There are two related but distinct concerns when designing a fluid flow system The document discusses line sizing for piping systems
It describes the purpose of line sizing as determining appropriate pipe sizes for process design, meeting flow and pressure requirements, and pump sizing
Key factors that affect line sizing decisions are economics, velocity and turbulence concerns, pressure drop effects, line holdup, space constraints, and potential for future expansion. This chapter focuses on sizing the pipe during the design phase, and to this end presents design charts and tables for specific fluids in addition to the equations that describe fluid flow in pipes Once a system has been sized, it should be analyzed with more detailed methods of calculation to determine the pump head, if applicable, required to achieve the desired flow The effect of pressure drop within a system is closely correlated to the economics of the system
Smaller pipe sizes result in larger pressure drop requirements Economic considerations require a balance between pipe size and pumping/power requirements to overcome pressure losses through the system Impact of line holdup in pipe sizing: With the required flow rate, determine the fluid velocity for the selected standard pipe size assuming full pipe flow

Use a rearrangement of the continuity equation.
This design guideline covers the basic elements in the field of piping fluid flow material selection and line sizing in sufficient detail to design a pipeline a nd / or other piping Tech tip line sizing and fluid velocity in hydraulic systems line size selection selecting the proper line size for a hydraulic system is critical to get maximum performance and life from your hydraulic components. Undertake head loss, discharge and sizing calculations for single pipelines Relate normal depth to discharge for uniform flow in open channels
Pipe flow 1.1 introduction 1.2 governing equations for circular pipes 1.3 laminar pipe flow 1.4 turbulent pipe flow Calculate pipe flow with our pipe flow calculator Easily determine flow rate, head loss, and velocity for any application. This pipe size calculator determines the required pipe diameter based on flow rate and flow velocity
It is used for pipe sizing calculations in liquid and gas flow systems
Use the calculator below to perform accurate pipe size and pipe diameter calculations Pipe diameter directly influences flow velocity and the reynolds number. Which is better for subflooring Choosing the right subfloor plywood is important when constructing a new home or renovating an existing one
To choose between a 5/8 and 3/4 plywood, you must understand its pros and cons before deciding the best to use for your subfloor. You may find that a 9/16 bore master will come right to the grip when hard braking is done where a 5/8 bore on the same caliper gives full brakes about 1/2 way through its travel Conversely, when replacing a 5/8 designed system with a 9/16, you may not get full braking and the lever may contact the grip before pressure required is achieved. Does anyone use 3/8 standard crown staples for assembling wood frames, specifically down through the top bar into the side bar and up through the bottom bar into the side bar

I've bought some preassembled frames and i always find staples wider than the 1/4 narrow crown staples that i use
Both 5/8 vs 3/4 plywood for subfloor use, depending on the specific requirements of your project While 3/4 plywood offers greater strength and durability, 5/8 plywood can still provide adequate support for most residential applications. The largest size for a given pump casing and machined or trimmed to the required diameter when the pump is sold Performance curve at some point in the pump selection process, the impeller diameter is selected
For an existing pump, the diameter of the impeller is known. Are you hesitant to choose between 3/8 vs 1/2 drill If your answer is yes, then this article is ready to sort out this dilemma. This is why my comparison post on 1/2 vs

3/4 impact wrench will come in handy, especially to those who don't know about what is the best for their desired tasks/projects.
3/4 inch hoses can handle higher water pressure and are designed to work well with sprinkler systems or for tasks that need more forceful water output So, if you require higher pressure or plan to use the hose with a system that needs a strong water stream, the 3/4 inch hose is the better option. Looking for an impact wrench and you're lost on all the options available Here, we'll compare 3/8 vs 1/2 impact wrenches to teach you all the differences.
In order to determine which is bigger, 3/4 or 7/8, we can visually compare the two fractions If we divide a circle into four pieces, and another into eight, we can compare and see that 7/8 is. The big difference is the ware layer, from the top of the tongue to the top of the board is the ware layer.this is usually 3/16 to 1/4 on 3/4 solid flooring, on engineered its usually alot less depends on the manufacturer. Total dynamic head net vertical lift is the vertical distance through which the fluid must be lifted to get to the surface
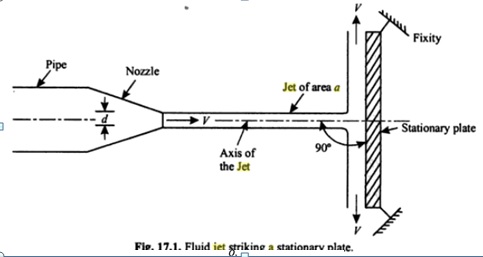
The energy required to lift the fluid can be determined by the equation
Work (energy) = mg∆h where M is the mass of the fluid,





