Future Smart Grids To Be Controlled By Units From This Electrical Panel Shop Characteristics And Horizons
Traditional power grids aren't designed to meet the demands of the future of smart grid technology The electric grid we have known for more than 100 years is being challenged in new ways by cybersecurity incidents, increasing demand, newer generation resources, and weather events. As renewables scale and energy consumption shifts, driven by electric vehicles, ai data centers, and electrified industry, aging infrastructure is falling behind
Smart grids characteristics and future horizons
Blackouts, rising costs, and energy waste signal a system under growing pressure. Our support of grid technology upgrades is even more important for the 21 st century grid Utilities also benefit from a modernized grid, including improved security, reduced peak loads, increased integration of renewables, and lower operational costs
Many grids are already 'smart'
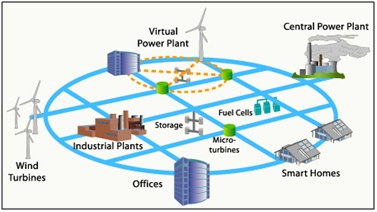
Smart grids are electricity networks that use digital communication, sensors and automation to monitor, control and optimise the generation, transmission, distribution and use of electricity in real time However, as grid operators now teeter on the edge of widespread ai adoption for load forecasting and demand curve calculations, ai could make smart grids. Microgrids complement smart grids by offering localized energy solutions that combine power generation, energy storage, and load management. Discover what smart grids are, how they work, and their benefits
Complete 2025 guide to intelligent electricity networks, renewable integration, and grid modernization. Artificial intelligence techniques for stability analysis and control in smart grids Methodologies, applications, challenges and future directions In the context of smart grids, power electronics enable the efficient and reliable transmission and distribution of electricity.

Their ability to improve efficiency and revolutionize power conversion systems makes them critical to the sustainable future of electricity
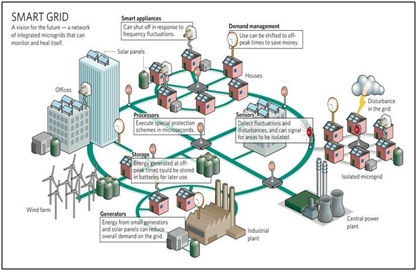
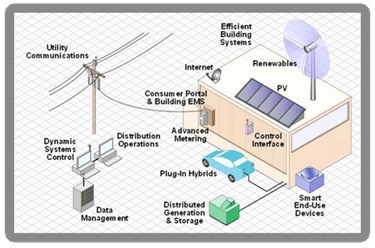
The general architecture of smart grids includes sensors distributed along the network, advanced measurement units, reliable communication systems and a centralized control system. By optimizing energy distribution and reducing waste, smart grids can lower the cost per unit of electricity for consumers while improving reliability. Even on small scales, the proposed benefits of the smart grid are substantial in maintaining sustainable energy use with growing demands In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of smart grid technology, specifically focusing on the challenges presented by cybersecurity, interoperability, and renewable energy integration.
Smart grids mark a significant evolution in how electricity is distributed and managed This boosts efficiency and strengthens grid. Electrical engineering is at the heart of modern innovation, driving advancements that impact industries and daily life As technology evolves, engineers are pushing the boundaries of what's possible
The potential exists for similar transformation and opportunity in the provision of electricity embodied in a concept known as the smart grid
The smart grid is defined as the system that delivers electricity from suppliers to consumers using digital technology to save energy, reduce cost, and increase reliability and transparency Like the telecommunications and internet revolutions that. This is commonly name as power grid Since the use of electricity, globally electric grids have similar structure, dynamics and principles even with the advancement of technology.
Smart grids transform electricity management with ai and iot, boosting efficiency, integrating renewables, and enable a greener, more reliable future Smart grids are the next generation of electricity management, combining advanced technology with energy distribution to improve efficiency, reliability, and sustainability. The main point to underscore is that in smart grid 2.0, actuators, coupled with increased intelligence to control the grid and meet the expectations on the grid, are needed. Abstract smart grid is the new trend for clean, sustainable, efficient and reliable energy generation, delivery and use
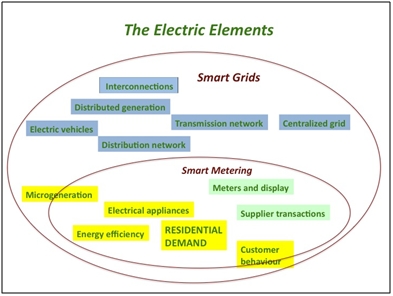
To ensure stable and secure operation is essential for the smart grid, which needs effective stability analysis and control.