Understanding The Axial Load Capacity Of The Modern Industrial Collar Shaft Carrying Evolution
Collar resistance to axial motion on the shaft is primarily a function of screw size Unlike traditional shaft collars, flanged shaft collars feature an extended flange on one side The tables indicate maximum static load that a collar will support without slippage.
Industrial Shaft Collar at Best Price in Howrah, West Bengal | R. B
Single or double piece clamp style shaft collars are used to provide axial location on, or for, shafts Understanding flanged shaft collars flanged shaft collars are mechanical devices that are used to secure rotating shafts in place I have found them particularly useful when trying to design shafts and axles which require a minimum of lathe turning operations.
The primary function of a shaft collar is to retain its position on a shaft
The amount of axial load (pounds or newtons) required to initiate slippage of a properly installed collar is defined as the axial holding power. Important specifications to review when selecting collars include Measured in pounds (lbs) or kilograms (kg), axial load capacity is the maximum load that can be applied along or parallel to and concentric with the primary axis Collar tightening action is applied in axial direction from the front, effective where radial access is limited
Bearing axial load is the force applied parallel to the axis of a bearing or mechanical shaft Unlike radial loads, which act perpendicular to the shaft, axial loads push or pull along the shaft's length. In robotic assemblies, collars secure arms and gears at exact positions, preserving calibration The best collars offer high axial load capacity and do so without damaging the shaft surface.

Threaded collars and shafts have much greater axial load capability
The tables also indicate typical maximum values and are not a guarantee under all conditions. In this article, we will discuss key considerations for engineering design related to axial load, including the calculation of axial stress and strain as well as the concept of critical load and buckling. Measured in pounds (lbs) or kilograms (kg), axial load capacity is the maximum load that can be applied along or parallel to and concentric with the primary axis. Threaded clamp collars provide a greater amount of axial holding capacity on threaded shafts
The design fully engages the thread for secure locking. Explore axial piston pump technology This guide covers hydraulic pump principles, variable displacement, open circuit designs, pressure range, and more. The primary purpose of a shaft collar is to resist an axial load

That is to hold itself in place despite pressure along the axis of a shaft
The axial holding power is primarily a function of screw size and applied torque However, other factors such as presence of oil, temperature, and the finish and hardness of the shaft can impact the holding power. The load capacity of a thrust bearing determines its ability to support axial loads without deformation or failure Engineers should carefully assess the anticipated loads in the application and select thrust bearings with adequate load capacity to prevent premature wear or damage.
Axial holding power the primary function of a shaft collar is to retain its position on a shaft Qkeyless bushing mechanism features clamping force increased up to 2.2 times *d35 is used for comparison Compared with the conventional shaft collars, these collars can clamp the shafts firmly.drefer to clamping force data on p.236 Easy installation in limited spaces collar tightening action is applied in axial direction from the front, effective where radial access is limited
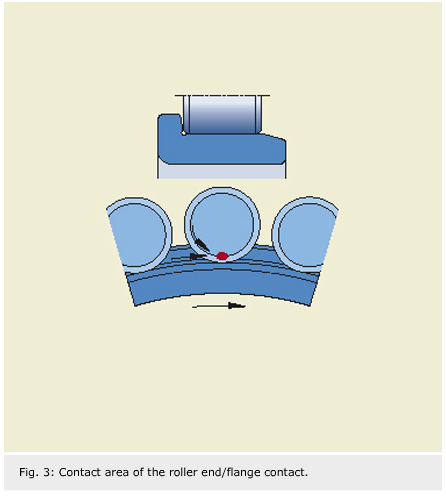
Understanding axial load and why it matters axial load is a force that pushes or pulls along the centerline of a rotating shaft
In many mechanical systems, axial forces are unavoidable due to pressure differences, gear engagement, or directional motion If axial loads are not properly managed, they can cause: Axial load capability collar resistance to axial motion on the shaft is primarily a function of screw size The tables indicate maximum static load that a collar will support without slippage
It is based on screws at full recommended seating torque and, for set screw collars, shaft hardness not exceeding rockwell c35. Thrust bearings thrust bearings handle axial loads, which are forces parallel to the shaft axis They are crucial in applications where axial stability is critical Types of thrust bearings thrust ball bearings
Suitable for high axial loads, these bearings are often used in gearboxes and pumps.
When the application load and speed exceed the capacity of ball bearings, roller pillow block bearings are typically specified Like ball bearings, roller bearings can carry a combination of radial and thrust loads.