Solar Engineers Debate The Friction Coefficient Of Rod End Bearings For Journal Extrudesign
The friction in a spherical plain bearing or rod end depends primarily on the sliding contact surface combination, the load and the sliding velocity To that end, skf has released a more advanced friction model that will help engineers select the most appropriate bearing for a particular application. Because there are so many influencing factors that are not mutually independent, it is not possible to quote exact values for the coefficient of friction.
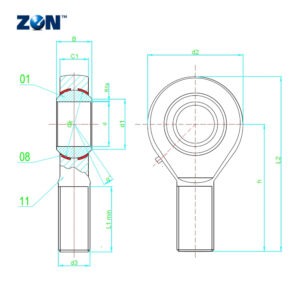
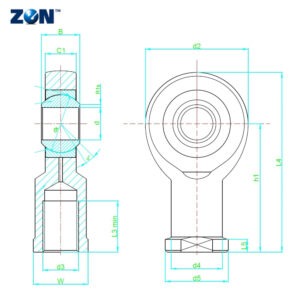
Requires Maintenance Rod End Bearings - Male Thread - Aire Bearings
Rod ends & spherical plain bearings ldk 4 Using a friction model as an engineering tool understanding friction in rolling bearings helps save energy and optimize bearing performance Service life the service life of the spherical plain bearings and rod ends operated under mixed or dry friction conditions is determined by the increase in bearing clearance or bearing friction caused by progressive wear of the sliding surfaces, plastic deformation of the sliding material or fatigue of the sliding surface
The friction coefficient between the connecting rod big end and the bearing is the final parameter to be investigated
For the baseline case, a coefficient of 0.1 is initially set, and then values of 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.6 are tested. Low coefficient of friction ranging from approximately.02 to.10 The coefficient decreases as load and temperatures increase (see chart) However, the coefficient also increases as surface speed and mating surface roughness increase
In conclusion, the friction coefficient of a rod end bearing is a critical factor that can significantly affect its performance By understanding the factors that influence the friction coefficient and choosing the right bearing for your application, you can ensure smooth operation, longer bearing life, and improved efficiency. Bearing bore diameter, mm the dynamic friction coefficient for rolling bearings varies with the type of bearing, load, lubrication, speed, and other factors For normal operating conditions, the approximate friction coefficients for various bearing types are listed in table 10.1.
Bearing friction and failure mechanisms 8.1 friction in rolling bearings the total friction torque acting on the bearing is caused by the bearing loads, viscous friction of oil, and seals of the bearing:
Learn how the coefficient of friction in bearings impacts performance, efficiency, and lifespan Explore materials, lubrication types, and design. The shear area reduction mechanism for textured hydrodynamic bearings was confirmed This work investigates the mechanisms for friction reduction in textured journal bearings
Coefficients of friction for different bearing types are shown in table iii If a more accurate calculation of bearing friction taking into account the effects of speed and lubrication is required for an application, please contact american's sales department. Friction for bushings, thrust washers and stripsload, sliding velocity, operating temperature are primary factors in determining the friction in plain bearings Friction is also influenced by the roughness of the surface on which the bearing runs, the degree of contamination and the lubrication conditions
The range of the friction coefficient µ for each bushing, thrust washer and stripe.
The following equation of karl von terzaghi, the father of soil mechanics, is one of the first and most commonly used theory when evaluating the ultimate bearing capacity of foundations. The bearing attaching each wheel to the cart is a lubricated steel on steel (kinetic coefficient of friction =.05) journal bearing with a shaft one inch in diameter. Tribological events that influence wear and its variations effect experimental results In this study, friction coefficient as example at bronze radial bearings has been determined by a new approach
In experiments, friction effects of bearings have been examined at dry and lubricated conditions and at different loads and velocities. You'll find rod ends in automotive steering systems, suspension linkages, aircraft control mechanisms, and industrial automation assemblies—essentially anywhere you need movement with adjustability in a confined space Rod ends are appreciated for their compact footprint, flexibility, and ability to absorb shock. Technical notesbearing slackness bearing slackness or bearing clearance is the dimension by which the inner ring can be moved within the bushings in a radial or axial direction when not installed and unlubricated

Rod ends and spherical bearings are manufactured with differing bearing slackness, as shown in the following charts, depending on the friction pairing and the size of the bearing.







