Precision Data: Why 1 11/16 To Mm Accuracy Is Essential For Submersible Tech What A Machining Ve And It
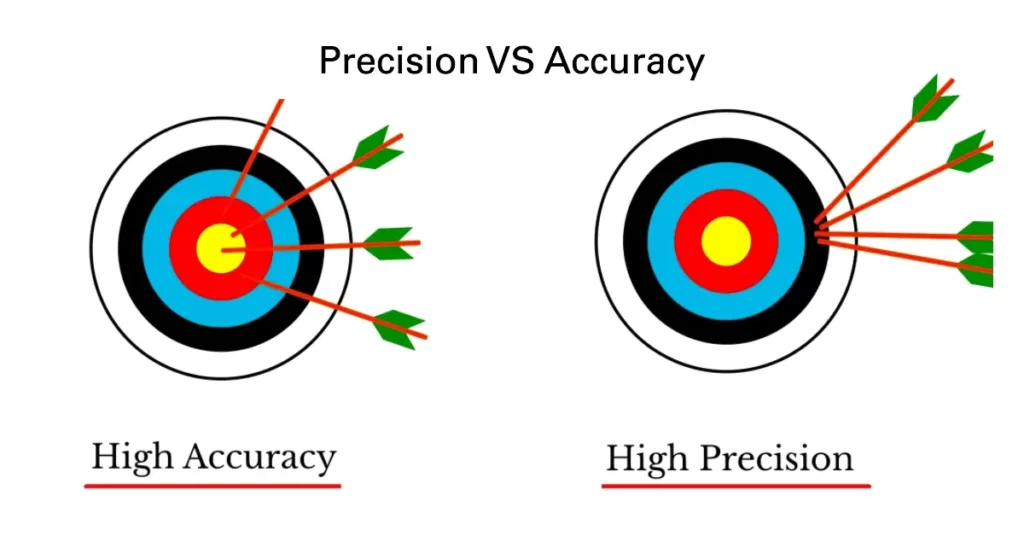
Understand the core principles of industrial measurement—accuracy, precision, and repeatability While both accuracy and precision are independently important, in the world of measurement, their combination is imperative. Learn their definitions, importance, differences, and how to improve them for reliable and efficient industrial processes.
IMarEST | How to Improve the Accuracy of Inclination of Semi
The benefits of accurate tool measurement 1 At its core, accuracy measures how close a result is to the. Improved machining accuracy when tool length, diameter, radius and runout are measured to micron precision using a zoller tool presetter, every tool enters the machine with accurate and consistent geometry
In machining, reaching processing accuracy of 1 micron (mm) is both an industry benchmark and challenge
Achieve and sustain this level of accuracy requires skills far beyond that offered by advanced. In the context of instrument and measurement techniques, precision is essential for ensuring the accuracy of the data collected. Accuracy refers to the degree of closeness between a measured value and the true value of a quantity Precision, on the other hand, refers to the degree of consistency or reproducibility of a measurement
While accuracy and precision are often used interchangeably, they are distinct factors that are important in manufacturing processes. Precision and accuracy one of the key reasons micrometers are essential for precision measurement is their exceptional accuracy Unlike traditional measuring tools like rulers or tape measures, micrometers offer a level of precision that is unmatched. Accuracy and precision are essential to ensure safety, compliance, customer satisfaction and the business's reputation

Hence, precision measurement is ubiquitous throughout manufacturing and engineering
Using accuracy and precision with an understanding of accuracy vs Precision as distinct metrics, it is important to consider their. Sometimes manufacturers get confused between precision and accuracy concepts This confusion in turn can lead to material waste and create additional costs while causing project delays
Therefore in this blogpost we will cover important differences between precision and accuracy along with their advantages In simple terms precision demonstrates repeatability and consistency. An important factor in the accuracy and precision of measurements involves the precision of the measuring tool In general, a precise measuring tool is one that can measure values in very small increments.
Accuracy and precision are crucial properties of your measurements when you're relying on data to draw conclusions.
Accuracy and precision are two essential concepts in science, mathematics, and engineering Understanding the difference between them and how to calculate these values is crucial for evaluating the quality of measurements and experiments. The scale on the right is a mm scale, and you know the marker is greater than 16 mm and less than 17mm, and you would report it as 1.67cm (which is the same as 16.7mm) Figure 1 b 2 2
A cm scale (left) and mm scale (right). This article delves into the significance of data quality, the various aspects that define it, and methods to improve it. Essential tools for precise joinery cuts joinery tools include routers, chisels, jigs for clean seamless vanity edges Dull tools gap joints, weakening 30%

Identify the number of significant digits in value
Solve problems that involve various calculations and report the results with the appropriate number of significant digits Apply proper rounding rules to computed quantities define accuracy and precision, and use accuracy and precision to describe data sets. To measure the volume of liquid in this graduated cylinder, you must mentally subdivide the distance between the 21 and 22 ml marks into tenths of a milliliter, and then make a reading (estimate) at the bottom of the meniscus Refer to the illustration in figure 1 5 1.
Understand the crucial difference between accuracy and precision in measurement, classification, and lidar systems Optimize performance and manage errors for reliable data. You'd trust a hardware store yardstick to measure and cut a fence post, but not to check a precision aerospace or medical component—and that's so even if the yardstick had hashmarks to 1 µm apart Its resolution wouldn't really reflect its accuracy.

Understanding and managing both systematic and random errors are essential for maintaining high accuracy and precision in manufacturing processes, leading to better product quality and customer satisfaction.
Knowing why precision, accuracy, and validity are vital in researchhelps students, staff, lecturers, and researchers do their work Without these guiding principles, increasingly complex experiments would fall apart and have no direction. Discover methods for precision data analysis, from cleaning to advanced modeling Accuracy is a fundamental concept that defines the degree to which a measurement, calculation, or prediction aligns with the true or expected value






