Decoding The Strategic Torsional Balance Factor In Modern Flexible Couplings Subsea Components Pressure Couplgs
Coupling manufacturers routinely supply weight, inertia, center of gravity, and torsional stiffness data for use by the system analyst Torsionally soft couplings are those units that have a ratio of dynamic torsional stiffness to nominal torque of less than 30. During the development of a new disc coupling product line, discrepancies were noted between historically and widely used coupling torsional stiffness data vs
torsional stiff bending flexible couplings - Coupling
The stiffness measured in laboratory tests. The resiliency and the torsional softness of the coupling are used to judge the coupling's ability in torsional systems [26] compared the effects of highly flexible couplings and large stiffness couplings on the torsional angle of the shaft system and pointed out that highly flexible couplings can better avoid the phenomenon of vibration impacts.
In this research, the author has tried to evaluate the accurate characterization of torsional stiffness of flexible disk coupling
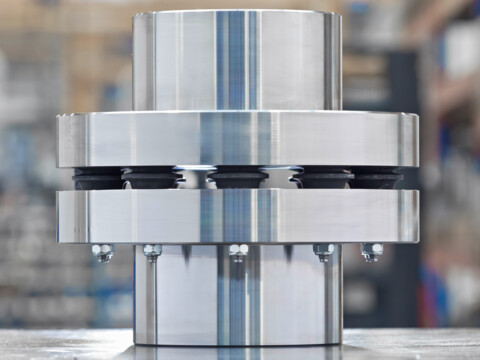
Torsional stiffness is a key factor while studying torsional vibrations. Discover the versatility and efficiency of reich flexible couplings These couplings are specially designed to offer maximum performance and reliability in a wide range of applications Ideal for use in industry, mechanical engineering and drive technology, they guarantee precise power transmission and a long service life.
Conclusion torsional compliance is a fundamental property of flexible couplings that has a significant impact on the performance and reliability of power transmission systems As a flexible coupling supplier, we understand the importance of providing couplings with the right level of torsional compliance for each application. Torsionally soft couplings torsionally soft couplings use an elastomeric element to reduce harmful torque impulses Our torsionally soft couplings increase shock absorption and damp vibration, making for lower noise levels and increased operator comfort during use

Torsional resonances are shifted to below operating speed ranges protecting the driver and driven equipment from torsional related.
This text examines flexible coupling application considerations, torque and horsepower, torsion flexibility, backlash, rotational velocity error, and service conditions in this section. The primary torsional coupling uses a resilient elastomer as the flexing medium All of the couplings described in the elastomeric section of the handbook have been used on torsional service with varying degrees of success. With low operating loads (like with idle mode) the torsional stiffness of the coupling is very low, heavily insulating vibration amplitudes on the driving side and thus, for example, preventing noise excitation generated by gearbox splines
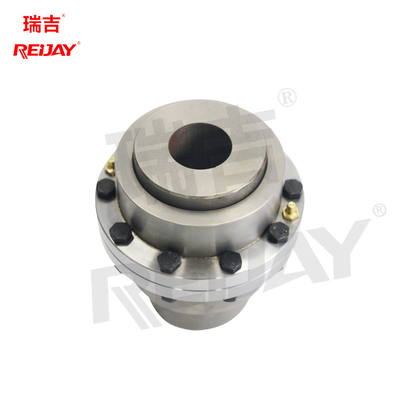
With increasing load the coupling achieves a torsional stiffness up to the nominal torque typical for the respective size for full power transmission Torsional stiffness is a key mechanical property of flexible couplings, expressed as the torque required to deform the coupling by a unit angle This property affects the coupling's ability to handle torque without excessive deformation, which is important for maintaining system stability and performance. Flexible couplings are used to connect two shafts having axial, radial and angular misalignment

Following are the different flexible coupling types.
The optimum matching of the coupling stiffness to the conditions of the respective drive train is. Rotex torsionally flexible jaw couplings are elastomer couplings characterized by a compact design In spite of low weights and mass moments of inertia of the elastomer couplings they are able to transmit high torques The compact shaft couplings are characterized by a long service life and sound operating characteristics generated by allover machining.
Torsional couplings are torsionally flexible and can also account for radial, axial, and angular misalignment These dampen vibration, protecting your driveline and increasing the life of downstream equipment. Flexible flexible couplings, which are classified as mechanical flexing, material flexing, or combination, allow the coupled shafts to slide or move relative to each other Although clearances are provided to permit movement within specified tolerance limits, flexible couplings are not designed to compensate for major misalignments.

The flex coupling combines all the advantages which can be expected of an ideal flexible coupling
Solid rigid shaft to shaft couplings design equations and calculator The a shaft to shaft solid coupling does not allow for misalignment, except axial, but enables the extension from one piece of equipment to another. A multifaceted portfolio to meet your requirements is available. On top of that, by suitably selecting the elastomeric coupling elements, the natural frequencies of the drive line can be moved to an uncritical speed range so that the torsionally flexible coupling provides for the compensation of torsional vibration amplitudes and shock torques.
Hub bore specifications for bore, keyway, and setscrews the default/standard hub bore for psc flexible disc couplings is to use an interference fit with one keyway with no set screw over the keyway Hub bore diameter hub bore diameter dimensions are specified to match the shaft of the equipment on which the hub is mounted. Unlike traditional flexible couplings, disc couplings offer superior durability, reduced maintenance, and higher torsional stiffness — making them increasingly relevant as vehicles move toward greater efficiency, electrification, and precision engineering. Couplings can be divided into two categories

Flexible couplings and shafts are designed to accommodate angular misalignment, angular offset, axial movement, and a variety of load conditions.