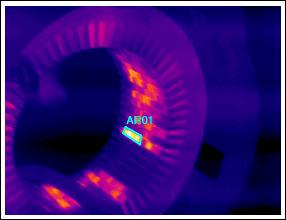
Core Loss Data: Which Induction Motor Parts Waste The Most Energy? Difference Between Synchronous And
This study describes a technique to determine the core loss in different parts of an induction motor (im) for any types of electric power supply The calculation tool functions in different operation modes in where voltage, frequency, torque and temperature are variables. To calculate the core loss, flux density waveforms ar.
Losses in Induction Motor
The fixed losses are core loss and mechanical loss, and the variable losses are copper loss and stray loss This thesis introduces an analytical loss calculation tool which is able to predicate the loss components and efficiency of a specific 5 kw induction motor powered by a converter In this article, we will discuss in detail the losses in induction motors.
Power flow diagrams show the stages of electrical power conversion to mechanical power, highlighting different losses
Efficiency is defined as the ratio of output power to input power, important for assessing motor performance. Induction motor losses and efficiency Understand fixed & variable losses Calculate efficiency—optimize performance and reduce energy waste now.
The major loss components of the induction motor Stator copper losses, rotor copper losses, iron losses, mechanical losses and additional load losses are presented here as a function of the rated. It outlines different types of losses—such as copper, core, mechanical, and stray losses—and explains how these affect overall motor performance and how efficiency can be calculated. What about core loss in lamination assemblies

Most published data evaluates only a single sheet when discussing core losses in lamination steel
But what happens when you stack them In the example above, laminations start to falter at as low as 60 hz compared with somaloy 700 3p, a popular smc material. Did you know that core losses in electric motors can account for as much as 20% of the total energy losses in industrial motor applications This loss, often unseen and misunderstood, affects efficiency, productivity, and overall performance in many applications, from manufacturing plants to electric vehicles.
An induction motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy During this process of electromechanical energy conversion some part of input power is lost in the form of electrical losses and mechanical losses in different parts of the induction motor. We have discussed this process in detail in the working of three phase induction motor All the core losses, friction losses and windage losses remain constant and these losses together are termed as constant rotational losses
The losses which increase with an increase in motor load are called variable losses.
To calculate the core loss, flux density waveforms are determined in different parts of the motor Where losses occur energy efficiency is based on the losses inside the motor during power conversion from electrical to mechanical energy (see figure 2) The major loss is stator resistance loss (stator i2r), which is the product of the square of the current multiplied by the resistance of the stator winding. An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. The data for the laminations was based on the core loss at 60 hz for each of the two materials, then extrapolated using this core loss formula And here's the hysteresis loss and eddy current losses formula for the smc material In the hands of your smartest engineer (maybe that's you), this equation can calculate your core losses at any.

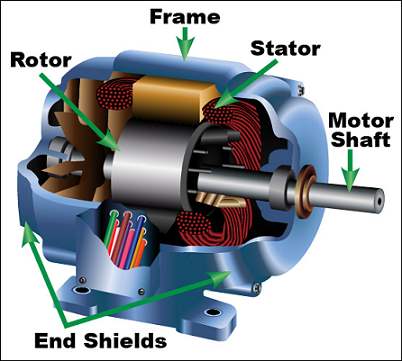
Induction motor has three main parts, rotor, stator and enclosure
The stator and rotor do the work and the enclosure protects the rotor and stator The stator is the stationary part of the motor's electromagnetic circuit and is made up of thin metal sheets, called laminations Laminations are used to reduce energy losses that would result if a. Quick start guide this sourcebook is designed to provide those who use motor and drive systems with a reference that outlines opportunities to improve system performance
It is not meant to be a comprehensive technical text on motor and drive systems Rather, it provides practical guidelines and information to make readers aware of potential performance improvements Guidance on how to find. Discover the 5 most common energy losses found in electric motors and some possible solutions, including the application of predictive maintenance techniques.

It is rugged and reliable, and is by far the most common motor type used in industry
These motors drive pumps, blowers and fans, compressors, conveyers and production lines For most countries the saving potentials for energy efficiency improvements in motor systems with best available technology lie between 9 and 13 percent of the national industrial electricity demand. Induction motor parts, known for their robustness and simplicity, stand as the workhorses in the industrial world Powered by electromagnetic induction, rather than direct electrical connections, these motors are pivotal in turning electrical energy into mechanical energy.
The leakage flux gets linked to other conductive parts of the motor such as the motor frame, bearings, and housing, and creates eddy currents that cause energy loss. In conclusion, minimizing core losses in electric motors, particularly induction motors, is vital for enhancing efficiency, performance, and longevity while reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.