Designers Debate Pbclinear Durability Versus Traditional Ball Bearings How Roller Differs From ? New Bearing
The majority of linear motion applications use one of three types of linear bearings Most slewing ring designs incorporate ball bearings or other rolling elements to ensure smooth rotational motion. Plain bearings, cam rollers guides, or recirculating ball bearings
Durability of MP bearings | Download Scientific Diagram
Of course, these are broad categories, and each one consists of many designs and variations with unique benefits These bearings typically comprise an inner and outer ring, made from robust materials such as carbon steel, chrome steel, stainless steel, brass, plastic, or anodized aluminum In this guide, we'll look at the technology behind each of the three main linear bearing types and compare the key performance.
Common types include ball bearings, roller bearings, needle bearings, drylin, plain bearings, and thrust bearings—each suited for specific load and environmental conditions
Whether you're building with linear shafts, bearing housings, or shaft supports, choosing the right type improves motion accuracy and minimizes maintenance. Linear ball bearings both plain bearings and ball bearings have advantages and disadvantages If you require more assistance, be sure to contact your local representative for more guidance on the linear motion bearing selection process. Learn what a linear bearing is, how it differs from a ball bearing, and how to choose the right type based on load, speed, and precision.
Opt for materials that match the operational environment for durability and efficiency. In this blog, we break down the mechanics of simplicity bearings and why they excel in. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of linear bearing design, covering fundamental principles, types, operating mechanisms, and key design considerations It explains how load capacity, speed, precision, lubrication, and environmental conditions influence performance

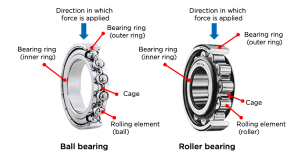
Linear slide bearings and linear ball bearings are two different types of linear motion guides, each with unique advantages, disadvantages and applicable occasions
Here is a comparison of the two types of bearings, as well as factors to consider when selecting. Ball bearing slew ring bearings (slewing bearings), with outer diameters from 80 mm to 310 mm, designed for applications requiring intermittent rotation while managing heavy radial, axial, and moment loads Featuring deep groove raceways and larger balls, these bearings ensure smooth rotation and can handle high moment, thrust, and radial loads Enhanced sealing systems, including larger seals.
Explore the pbc linear library of information for linear motion products such as linear bearings, linear shafting, linear slides, linear actuators and more. It then explores methods to calculate the statistical probability of life for various linear roller bearing solutions. Closed linear ball bearing with a 25mm id (inner diameter) Heat treated allow steel shell for durability, low coefficient of friction for speed and resin retainer for quiet motion.

Square flanged linear ball bearing, end mount with a 50mm iso metric inner diameter and double wide design for higher cantilevered load capacity
Interchangeable with linear ball bearings and some bronze bushings, they ensure durability across various applications. The be integrated ball screw linear actuator series exemplifies an innovative convergence of hybrid stepper motors with integrated ball screws and nuts, designed specifically to cater to the demanding requirements of engineers and designers for high torque, precision, and efficiency in linear motion applications.