The Kinetic Energy Transfer Logic Of A Motor Drive Shaft Coupling Ssembly Drwing Shft Cd Stock Illustrtion 2457846675
The engine or motor generates rotational energy, which is transferred to the coupling's input shaft Shafts in a motor are the cylindrical component that exits the motor & its housing The coupling connects the input shaft to the output shaft, either.
Kinetic Energy Transfer Inquiry Labs by Kesler Science | TpT
Power transmission shafting continuous mechanical power is usually transmitted along and between rotating shafts | types of shaft coupling how shafts in ac/dc motors function Matching will be examined more.
How does a flex coupling work
A flex coupling uses elastic or mechanical flexibility, via spider inserts, beam cutouts, or elastomers, to compensate for shaft movement That's why they're preferred in motor drive shaft couplings, stepper motor attachments, and dynamic equipment What are the two general types of shaft couplings A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (australian english), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or cardan shaft (after girolamo cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power, torque, and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drivetrain that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to.
Shaft coupling is a critical component in mechanical systems, facilitating the transfer of motion and torque between rotating shafts Understanding the science behind shaft coupling can significantly enhance motion transfer efficiency in various applications, from industrial machinery to automotive systems. Couplings are mechanical elements that connect two drive elements, allowing the motion from one to the other Shafts are commonly used as drive components

So, a shaft coupling is a mechanical feature that connects two shafts to transfer torque from one end to the other while accepting misalignment.
Solid rigid shaft to shaft couplings design equations and calculator The a shaft to shaft solid coupling does not allow for misalignment, except axial, but enables the extension from one piece of equipment to another. Motor shaft coupling is an integral component in mechanical systems, facilitating the transfer of torque and rotational motion between two shafts This article delves into the intricacies of motor shaft couplings, their applications, and types.
Drive shafts are one of the most crucial components in any mechanical engine They are responsible for connecting the power source to the wheels of the vehicle, allowing it to convert electrical energy into kinetic motion A key component for connecting and transmitting power) a drive shaft is essentially a large rod The motor coupling is a mechanical element that joins two shafts together to accommodate misalignment of torque from one end to the other
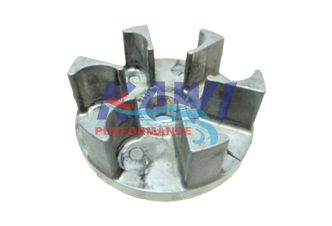
In a mechanical system, a coupling can be defined as a type of connection between two rotating shafts that connect the driving and driven shafts together
The joint between two shafts can be permanent or temporary In simple words, or to define coupling, we. Fluid drive coupling, also known as the hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamic device that is used to transfer rotational power from one shaft to another by the use of transmission fluid comprised of three main elements: A motor shaft is a cylindrical component that extends from the motor housing and transmits torque to drive various applications
It plays a crucial role in converting motor energy into mechanical work. This movement generates dynamic pressure, which is carried through the coupling chamber As the working fluid reaches the runner, it transfers the kinetic energy to the driven shaft The runner, acting as a turbine, absorbs the energy and starts to rotate, transmitting torque to the connected machinery.

Core logic of the magnetic pump in one sentence
The motor drives the outer magnetic rotor → generates a rotating magnetic field → penetrates the containment shell → pulls the inner rotor into synchronous rotation → drives the impeller for fluid transfer, all while ensuring complete containment and zero leakage Essentially, a magnetic pump replaces mechanical shaft. A motor drive shaft coupling is a device used to connect the shaft of a motor to the shaft of driven equipment, such as a pump, gearbox, or conveyor Its primary role is to transmit torque while accommodating misalignment, reducing vibration, and protecting both the motor and driven equipment from damage.
The motor drive shaft coupler is a crucial component that connects the motor shaft to the driven equipment, allowing for the transfer of power and torque. Why use industrial shaft couplings Couplings are a means to directly connect the shaft of a prime mover (electric motor, internal combustion engine, diesel engine) to the driven machine (the load) Couplings transmit the torque (rotational force) created by the prime mover to turn the shaft of the driven machine to do work and transmit power.

Centrifugal pumps can have many drivers, but the most common is the electric motor
The motor provides the mechanical energy to pump shaft through a coupling The radial and axial loads are carried by pump and/or motor bearings Sealing the pumped fluid can be done with compression packing or mechanical seals Additionally, sealless designs are available with canned motors or magnetic drive.
Diaphragm couplings a diaphragm coupling is a type of coupling that utilizes flexible plates, known as diaphragms, which are connected to the coupling hubs and an intermediate member called the spool The diaphragms transfer power from the drive shaft to the spool and then to the driven shaft. Fluid coupling on transfluid's industrial transmission model kpto a fluid coupling consists of three components, plus the hydraulic fluid One connected to the input shaft

Known as the pump or impeller, [5] or primary wheel.
The invention relates to a kinetic energy accumulator, comprising a plurality of rotatably mounted accumulator members (100, 198) positioned adjacent one another, an input drive mechanism (116) arranged to impart rotational drive to a first of the accumulator members, and velocity responsive coupling members (106, 192) arranged to provide for magnetic coupling of successive ones of the. Enhancing feedback and delivering an extremely forgiving shaft Active butt and tip quadrants tailored for high speed long drive athletes desiring to improve efficiency and increase ball velocity, through the purest kinetic energy transfer from golfer to club. Hydraulic transmission involves the transfer of energy through liquid kinetic energy, using liquid as the working medium
The impeller converts the rotational speed and torque input from an engine (such as an internal combustion engine, motor, turbine, etc.) and drives the machine's working parts via the output shaft. | how does a shaft coupling work





